 |
| Industrial wireless connections established outdoors across long distances have to consider transmission path geometry. |
Wireless transmission of process signals in industrial settings becomes more prevalent every year, and should continue to do so for quite some time. Many installations are part of networks operating similarly to the wifi you may have in your home, with multiple points communicating via a network control scheme of some sort. The facility is flooded with signal coverage through multiple access points, so there may not be much need to consider signal propagation. This is an oversimplification, but as an operator or implementer, making the actual signal connection is probably not going to be an issue in most cases.
What about the other cases?
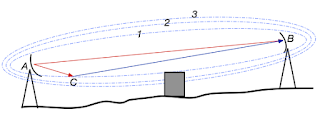 |
| Antennas with three Fresnel zones depicted and obstruction that is outside the primary Fresnel zone Courtesy Wikipedia |
An extended transmission distance across an outdoor area requires more understanding of signal propagation and factors that impede successful delivery of process data from transmitter to receiver. One concept that comes into play is the Fresnel zone.
Let's avoid an overly technical approach to Fresnel zones. The purpose of this post is to provide those with limited radio expertise familiarity with the subject of Fresnel zones at a level enabling visualization of the concept, and also to recognize its potential impact on achieving a successful wireless process connection.
We often consider the transmission path between two points to be the familiar "line of sight", an unobstructed straight line between transmitter and receiver. In practice, radio frequency transmission is more accurately characterized by Fresnel zones. Being aware of the shape of the first, or primary, Fresnel zone for your application is an important element in identifying potential obstructions. A general practice is to keep the primary Fresnel zone at least 60% clear of signal obstructions, in order to maintain high wireless link performance.
There are numerous sources of Fresnel zone calculators online, but a strong recommendation to consult with your selected wireless equipment provider is in order here. Combine their expertise at applying their products with your application knowledge to leverage an effective solution.
