Industrial wireless networks (IWNs) are a key enabler of many aspects of advanced manufacturing. IWNs promise lower installation costs compared with wired alternatives, increased operational flexibility, improved factory visibility, and enhanced mobility. Wireless networks are not dissimilar to wired networks with the key exception being the transmission medium. Wired networks typically operate over copper wires, coaxial cable, or fiber optic cable depending on the network type. Wireless networks operate without wires or cables using the electromagnetic propagation. As such, wireless networks operate within a shared medium that is publicly accessible. A listing of wireless technologies is listed below:
Home and Office
This includes standards-based communications system typically found in the office environment but may be useful for the factory. Includes IEEE 802.11 variants and Wi-Fi compliant devices. Bluetooth also falls into this category.
Instrumentation
Includes systems specifically designed for factory operation. IEEE 802.15.4 standards such as International Society of Automation (ISA) 100.11a, WirelessHART (IEC 62591:2016), IEC 62601, and ZigBee fall into this category. High-performance standards built on IEEE 802.11 include the Wireless Networks for Industrial Automation - Factory Automation (WIA-FA) IEC 62948. Many exceptional proprietary options exist as well.
Wide Area Sensing
Some applications require the ability to transmit over long distances with minimal power to conserve battery life for sensing and control over wide geographical distances. Examples include LoRaWAN and Sigfox as well as modes of 4G and 5G cellular radio standards.
Other commercial
This category includes systems such as satellite, cellular, directional microwave data links, optical (visible light), and land-mobile radio. This category includes technologies supporting video and voice communication.
Analynk Wireless manufactures hazardous area wireless access point enclosures and hazardous area wireless antennas. Analynk is also a certified UL508A panel manufacturer providing high quality control panels to Ohio and surrounding areas. For more information, visit the Analynk website here or call 614-755-5091.
Showing posts with label receiver. Show all posts
Showing posts with label receiver. Show all posts
Wireless Process Connections - DIY May Not Be Your Best Option
 |
| Analynk can design and fabricate complete systems for establishing wireless process connections. |
The Analynk application team can design and fabricate a complete package solution for your process measurement or wireless connectivity requirement. Share your ideas and challenges with the wireless and process measurement experts, leveraging your own knowledge and experience for a successful project outcome.
Use Signal Repeaters to Overcome Industrial Wireless Transmission Barriers
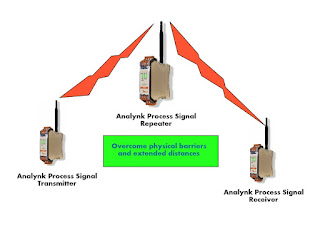 |
| A repeater can be used to overcome barriers to signal transmission, such as distance and structures. |
One, though not the only, solution to overcoming the challenge that can arise due to extended distance or substantial obstacles between the transmitter and receiver is the placement of a repeater. Analynk provides a repeater that can be strategically located between transmitter and receiver to extend the overall transmission distance, or route the signal around obstacles that may otherwise degrade the transmission. The data sheet included below describes how easy it is to apply and provides all the technical details.
Wireless connectivity is an incredibly flexible option for delivery of process data from measurement point to control point. Contact Analynk with your wireless communication challenges and get solid practical solutions.
It's Been A Good Year for Us.
 |
| Industrial wireless transmitter and receiver |
- Introduced several new hazardous area enclosures for wireless access point equipment.
- NEMA 4X designation on all explosion proof antennas
- Expanded line of specialty enclosures for wireless transceiver equipment
- New larger hazardous area rated RF enclosure for wireless equipment
- Custom designed OEM products or systems
- Continued expansion of 3D product drawing library
- Updated and expanded distributor network with seasoned professionals
Next year is already shaping up to be even better, with more innovative and creative products for establishing wireless process control connections across the room, across the property, and around the globe.
Creating Wireless Process Connections Is ABC Simple
Industrial wireless is not new, it is a mature technology. With the products available today, implementing a wireless process signal connection is no more difficult than installing a simple process controller. Analynk is a part of that simplicity, manufacturing modular receivers, transmitters, and companion products enabling operators at any scale to effectively deploy a 900 MHz or 2.4 GHz wireless solution.
There are many instances where a wireless solution provides distinct advantages over wired installations. Understanding the simplicity of wireless installations, and that product based solutions are readily available, can unleash your ingenuity at solving process control challenges using wireless communications. A previous article may help you recognize opportunities to avoid expensive or difficult cabling, or actually make connections you thought were impossible.
Let's look at a basic installation that measures temperature at a remote location (the measuring station) and transmits the signal to your office (the monitoring station).
Here is all you need:
The simple wiring connections to the transmitter and receiver differ little from those of most other devices (see the ABC’s on the illustration).
A - Connect a power source to operate the unit
B - Connect the input signal (if it's a transmitter) or output signal (if it's a receiver).
C - Connect discrete inputs (if it's a transmitter) or outputs (if it's a receiver).
Here is all you need:
- Power supply to operate the temperature measurement instrument and the Analynk transmitter. Analynk transmitters consume little power and can be provided with photovoltaic power supplies, if needed.
- Temperature measuring device of your choice with 4-20 ma output signal and up to two discrete outputs. It does not need to be wireless.
- Analynk transmitter located at the temperature measurement station to convert the 4-20 ma temperature signal to digital format and send it to the monitoring station. The connection between the temperature measuring device and the Analynk transmitter is wired.
- Analynk receiver located at the monitoring station to receive and decode the signal from the Analynk transmitter, converting it back to 4-20 ma. A wired connection between the receiver and your monitoring or recording equipment delivers the 4-20 ma temperature signal to its destination.
The simple wiring connections to the transmitter and receiver differ little from those of most other devices (see the ABC’s on the illustration).
A - Connect a power source to operate the unit
B - Connect the input signal (if it's a transmitter) or output signal (if it's a receiver).
C - Connect discrete inputs (if it's a transmitter) or outputs (if it's a receiver).
 |
| Wiring diagram for Analynk Model A753 wireless transmitter |
You can gang inputs and outputs together with an expander module and use a single transmitter and receiver to deliver multiple sensor signals. All units are DIN rail mounted with removable terminals for simple, organized installation and replacement.
Wireless connections can expand your operating capabilities, as well as business opportunities. Analynk has made the implementation easy. Use your creativity and ingenuity to bring new applications to your operation. Contact Analynk anytime to discuss your ideas or get the help you need to put your ideas into action.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
